How To Draw Yellow Diamond Rings
IGS may receive customer referral fees from the companies listed in this page. Learn more than.
Diamond Buying and the Four Cs, Role two: Diamond Color
For almost, color is probably the about familiar of the Four Cs of gem grading. However, diamond color grading is more disruptive than you think.
Larn about the GIA color grading calibration and how fluorescence and metal settings tin impact the appearance of diamond colors. Since the Iv Cs aren't as distinct as they may seem, we'll besides recommend the combinations of color, clarity, cut, and carat to expect for when ownership a diamond.
The GIA Diamond Color Scale
The Gemological Plant of America (GIA) color calibration for white or colorless diamonds ranges from grades D to Z. Any stone within that range falls inside the "normal color range."
The about highly valued diamonds accept no colour. Thus, the more than colour a stone has (yellow or brown), the lower the grade. Yellow or brown diamonds that go far by the Z grade, nonetheless, instantly become up in price. Such diamonds have enough color to be considered "fancy," along with pink, green, and blue diamonds. (One time these diamonds accept enough saturation to evidence these colors, they are automatically considered fancy).
Equally with other diamond grading scales, diamond value goes upwards exponentially with each increase in grade. (Conversely, value goes down exponentially as the color form decreases). Whereas diamonds of any carat size hold value and notice use, diamonds between L and V color grades appear less often in jewelry.
The GIA D-Z scale is divided into five categories:
- Colorless — D, Eastward, F.
- Nigh Colorless — M, H, I, J.
- Faint — M, L, 1000.
- Very Calorie-free — North, O, P, Q, R.
- Calorie-free — Due south, T, U, V, Due west, X, Y, Z.
White Diamonds
Of class, the almost valuable diamond color is D. A diamond of this form commands a premium only because of its complete boredom.
You are probably familiar with the idea of diamonds existence white. Still, 98% of gem-quality diamonds actually contain some amount of xanthous due to nitrogen impurities within the diamond.
Greatcoat Diamonds
All faintly yellow diamonds (not colorless and not fancy xanthous) are chosen "Cape diamonds." However, some jewelry lines volition specifically market only stones of lower color grades, K to Z, equally "Greatcoat diamonds" in guild to promote them equally affordable alternatives to "non-Cape" diamonds.
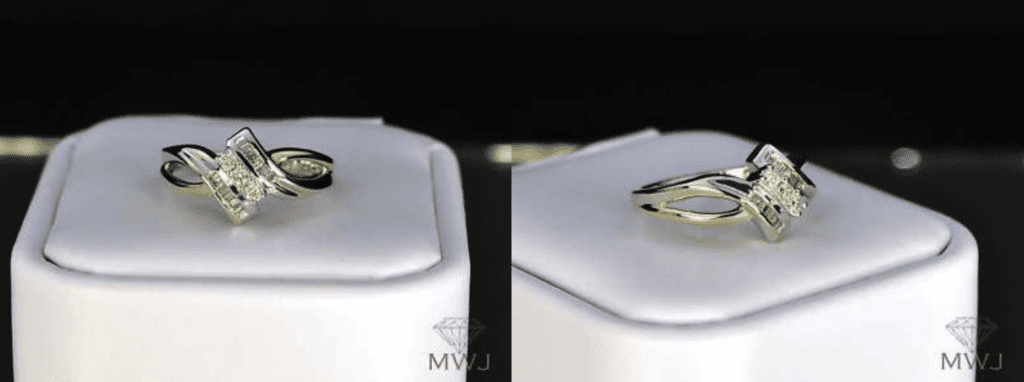
10K yellow and white gold date band with three circular primary diamond stones (0.03 cts each, J color, I2 clarity) and baguette emphasis stones (0.14 cts, K colour, I3 clarity). The diamonds, peculiarly the baguettes, announced quite yellow against the ring. K diamonds are in "Cape Diamond" territory. (If the metal around the chief stones had been yellow instead of white gold, the K diamonds would have been shown to greater reward). Photos © Midwest-Jewelry. Used with permission.
Lemonade Diamonds
Sometimes, vendors market place W-Z color form diamonds specifically every bit "lemonade" or near-fancy xanthous diamonds.
Diamond Color Grades as Ranges
Consumers and vendors pay a bully deal of attention to specific colour grades when a rock sits on the high end of the scale. Once colors move by M, withal, the grades are often given as ranges, such as U-V, W-10, and Y-Z.

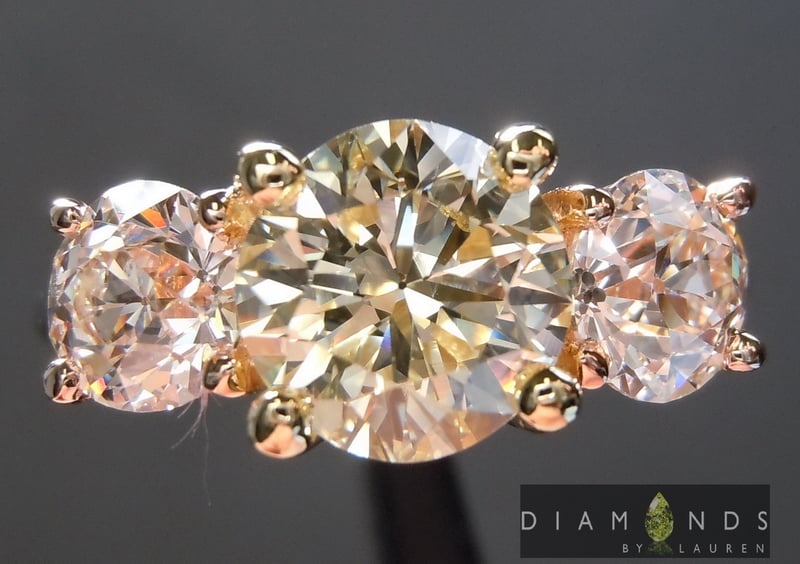
The gilded prongs enhance the yellow of this Y-Z diamond (ane.51 cts, SI2), while the white setting enhances the whiteness of the engagement band's side stones. © Diamonds by Lauren. Used with permission.
Diamond Colour Grades and Price Jumps
You'll discover an enormous price difference between a D and an E color diamond. The next biggest cost difference lies between an F and a G color diamond. That'south understandable, every bit G falls into the "virtually colorless" rather than "colorless" category.
Just as diamonds accept "magic number" carat sizes, they also have "magic alphabetic character" color grades. You can notice great deals just below them. For instance, K and H stones make great value choices. Although they're not much darker than F, they're much more than affordable.
Stones with I, J, and One thousand color are commercial quality. You'll commonly see them in most jewelry stores, but high-end stores can bear them, too.
The Result of Gold Colors on Diamond Colour
Stones in the I, J, and Chiliad range starting time to look faintly yellow or brown, especially in larger carat sizes. Jewelers can disguise these colors, however, by setting the gems in yellowish or rose gold. The color of the metal can make lower grade stones await whiter in contrast.

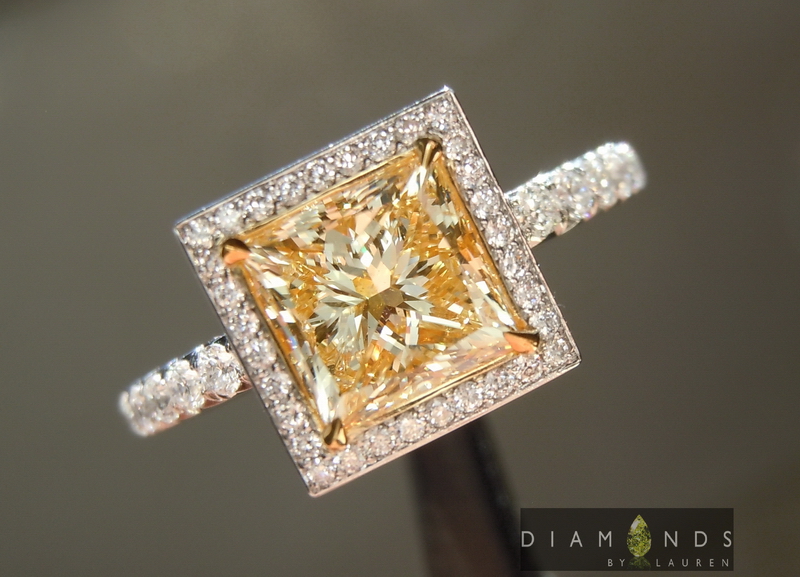
A light yellow center diamond (color grade U-V, VSI clarity) gear up in yellow golden to enhance the colour. The side stones, light brown diamonds (K color, VS clarity) set in rose gold, appear whiter in contrast. © Diamonds past Lauren. Used with permission.
Apply White Gold Settings for High Diamond Color Stones
Interestingly enough, yellow or rose gold settings practice the opposite for stones of higher color grades. For stones G and above, the reflections of yellowish or rose gold colors make the diamonds look warmer in tone. Therefore, a high-color grade diamond, if gear up in yellow or rose aureate, is wasted. This will make the diamond announced to have the same tone as a stone with a lower colour grade.
- For a yellowish or rose gold setting, purchase a lower color grade stone.
- For a white gilt setting, purchase a higher colour grade stone.
Settings with Multiple Gilt Colors
Of course, jewelers have become very conscious of the consequence of metal colors on gems. As a result, rings with shanks of ane colour and bridges or prongs of another accept get increasingly popular. For instance, someone who wants to enhance or preserve the white color of a rock tin set information technology with a white aureate bridge and prongs, while using xanthous or rose gold for the shank. This way, stones will announced whiter, whether high or low-colored, due to the white gold base beneath the rock, while the darker xanthous or rose gold color of the shank will make the stones appear even whiter in contrast.
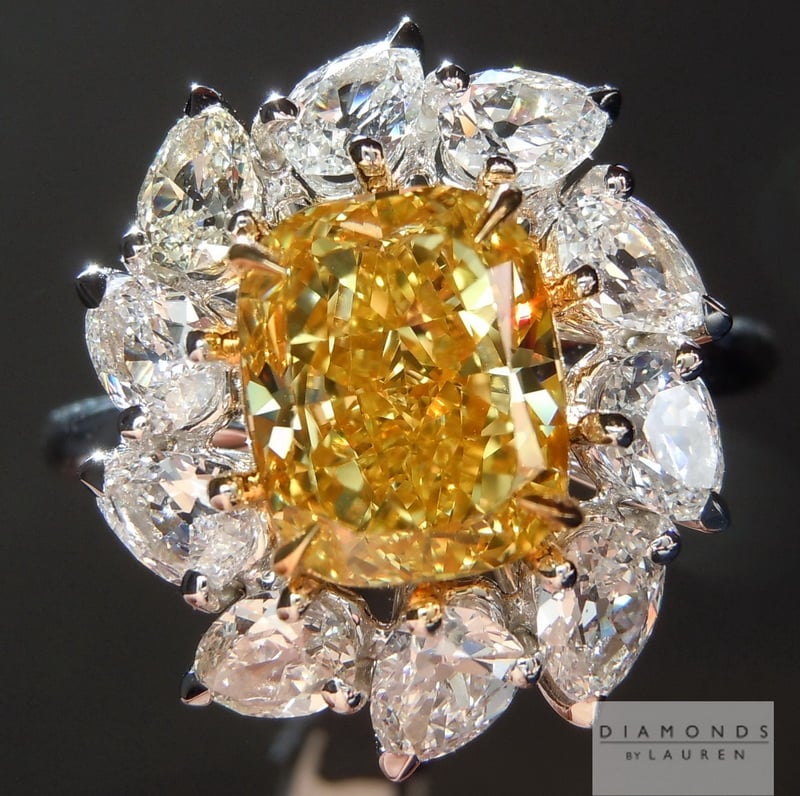

The gold prongs heighten the yellowish of this cushion-cut, fancy vivid yellowish (2.13 cts, VS1) diamond ring, while the white setting enhances the whiteness of the side stones. © Diamonds by Lauren. Used with permission.
Buying Diamonds Below J Color
Earlier purchasing a diamond below J in color, keep in mind that the dark-brown or yellow color will exist fairly noticeable. Generally, buying diamonds below J isn't advised.
Nevertheless, some people prefer the soft, mellow await of a faintly yellow diamond as opposed to the hard, icy brilliance of a white diamond. Perhaps for these consumers, the pale yellow colour has pleasant associations, such as candlelight. If this describes you lot, you yet shouldn't pay too much for diamonds of this color, despite the positive vibes they give.
If you're considering a diamond below I in color for budget reasons, fluorescence may be your friend.
The Aurora Butterfly of Peace diamond collection contains 240 natural, fancy colored diamonds, full weight 167 cts. Some of the stones are fluorescent. The collection is shown in daylight and nether ultraviolet light. Photos past Abronsteinwiki. Licensed under CC Past-SA three.0. (Slide testify created to highlight fluorescence).
Diamond Fluorescence
A third of all diamonds fluoresce, and 90% of fluorescent diamonds fluoresce bluish. In diamonds with high color grades, especially D-F, potent fluorescence is undesirable since it tin can make them appear milky.
Fluorescent diamonds with higher color grades cost 15% less than non-fluorescent diamonds. On the other manus, diamonds of I color and below really increase slightly in toll if fluorescent. Since blue is complementary to yellow, medium to stiff blue fluorescence can cancel out some of the yellowish color.

Nearly colorless diamonds will lose value if fluorescent. However, the octagonal-cut Portuguese Diamond actually gains value due to its uniquely intense fluorescence, combined with its large size (127.01 cts) and flawlessness. Fluorescence makes this diamond appear milky blueish even under daylight. Photo past Observer31. Licensed under CC By iii.0.
This toll boost is limited to blueish fluorescence because, needless to say, yellow or light-green fluorescence volition increment a stone's xanthous color. Notwithstanding, when a rock reaches the fancy color range, yellow fluorescence becomes desirable.
Professional Diamond Color Grading
For the boilerplate consumer, differentiating diamonds with color G and above proves hard. (Attempt it for yourself in this diamond color sorting quiz!) So, how do professional diamond graders tell the difference? They employ a master gear up of diamonds. These include stones representing the lightest possible color for each diamond color class.
Color Master Sets
When grading a diamond, professionals compare it with different stones in the master set. First, they place the two master stones between which the test rock's color lies. One is lighter than the test rock, the other darker. They then assign the exam stone the color grade of the lighter master rock. For case, if a test diamond's color lies between G and H, it's a G colour rock. (G is lighter than H. Remember that the master stone shows the lightest possible colour for its grade. Then, G has many slightly darker gradations before the colour reaches H).
Tabular array Down or Table Upward?
When evaluating diamonds in the normal color range, professionals place the stones table or face up downwardly. They do this because colour looks more concentrated through the pavilion, and graders look for lack of colour in these diamonds. In contrast, they course fancy colored diamonds table or face up. In these stones, graders look for a maximum amount of color.
White Light and Neutral Colors
The master set diamonds sit in a white tray shaped like an angular trough that can rock backwards and forwards. The white tray itself sits in a gray light box that shines white lite on the diamonds. Neutral colors are ever used during diamond grading, because diamonds reflect the colors around them. Even wearing blood-red, xanthous, blue, or other bright colors while grading volition throw off accurateness.
Diamond Colour and Recommendations for Other Diamond Qualities
- Ideally, pair diamond colors of D, East, or F with clarity grades of F (flawless), IF, VVS1, or VVS2, especially if the diamond matches or exceeds one carat in size.
- Diamond color of Thousand, H, or I should be paired with VVS2, VS1, or VS2 clarity. Pair J, Thou, and Fifty with SI1 or lower.
- A rock smaller than i carat tin can have a color grade of I, J, or possibly even M without appearing too yellow.
Assessing Diamond Colour Online
Merely similar clarity and cut, information technology'south essential to see the diamond'southward color before you purchase. Since color grades of colorless diamonds are based on body color, these grades can be misleading. What'due south important is the face up-upwardly color, which you can only approximate in accurate pictures or videos.
Both James Allen and Blue Nile provide shut-up, 360° videos of the thousands of diamonds in their inventory. This lets you judge for yourself if any of the Four C's is lacking.
Amend yet, James Allen has hundreds of examples of different colour diamonds in different ring settings. If you're not sure whether the colour will testify, see what others accept used in the same setting.
Source: https://www.gemsociety.org/article/diamond-color/
Posted by: morasuld2000.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Draw Yellow Diamond Rings"
Post a Comment